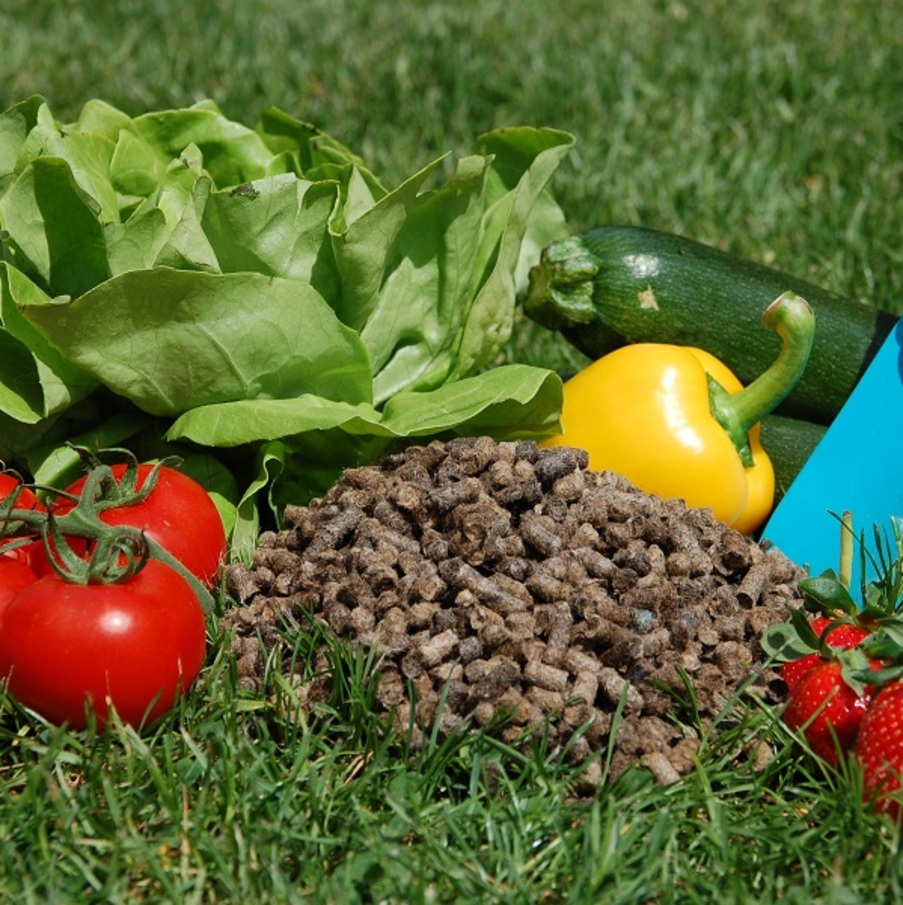
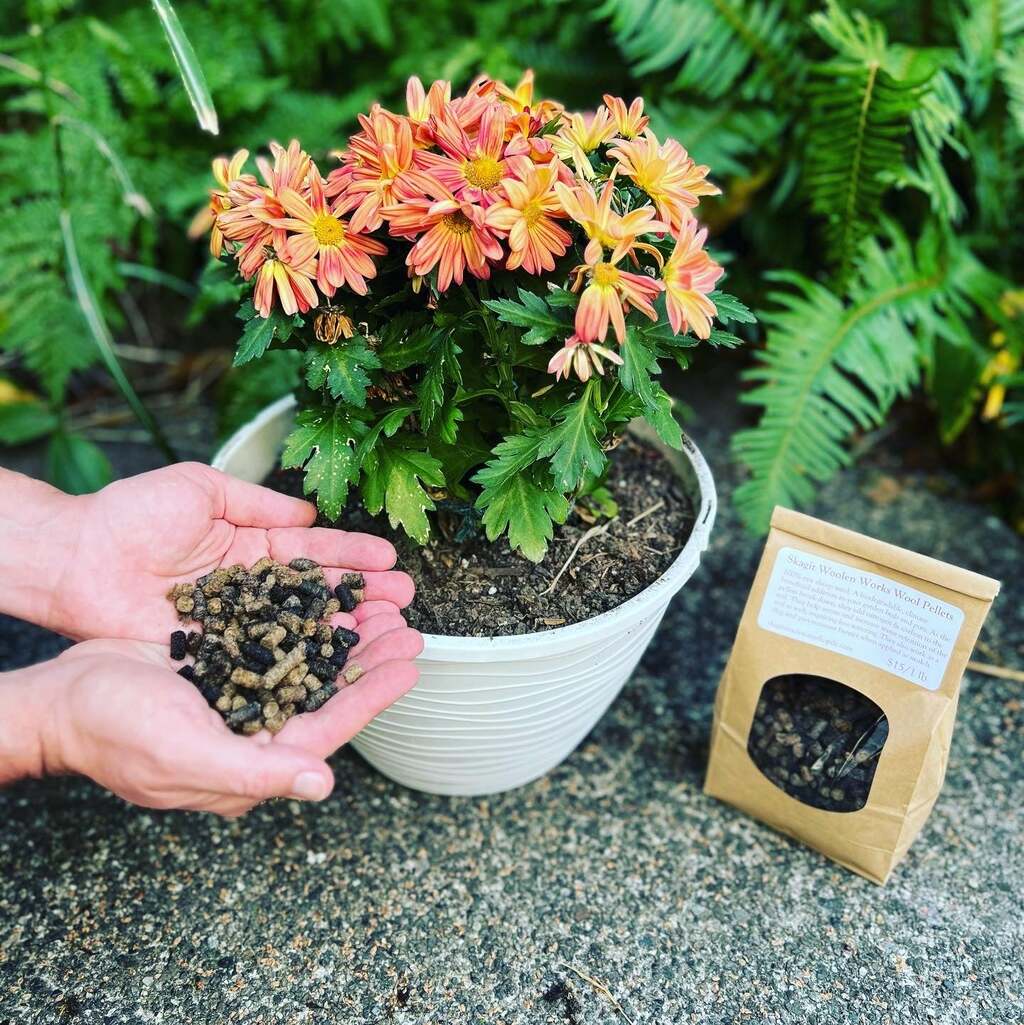
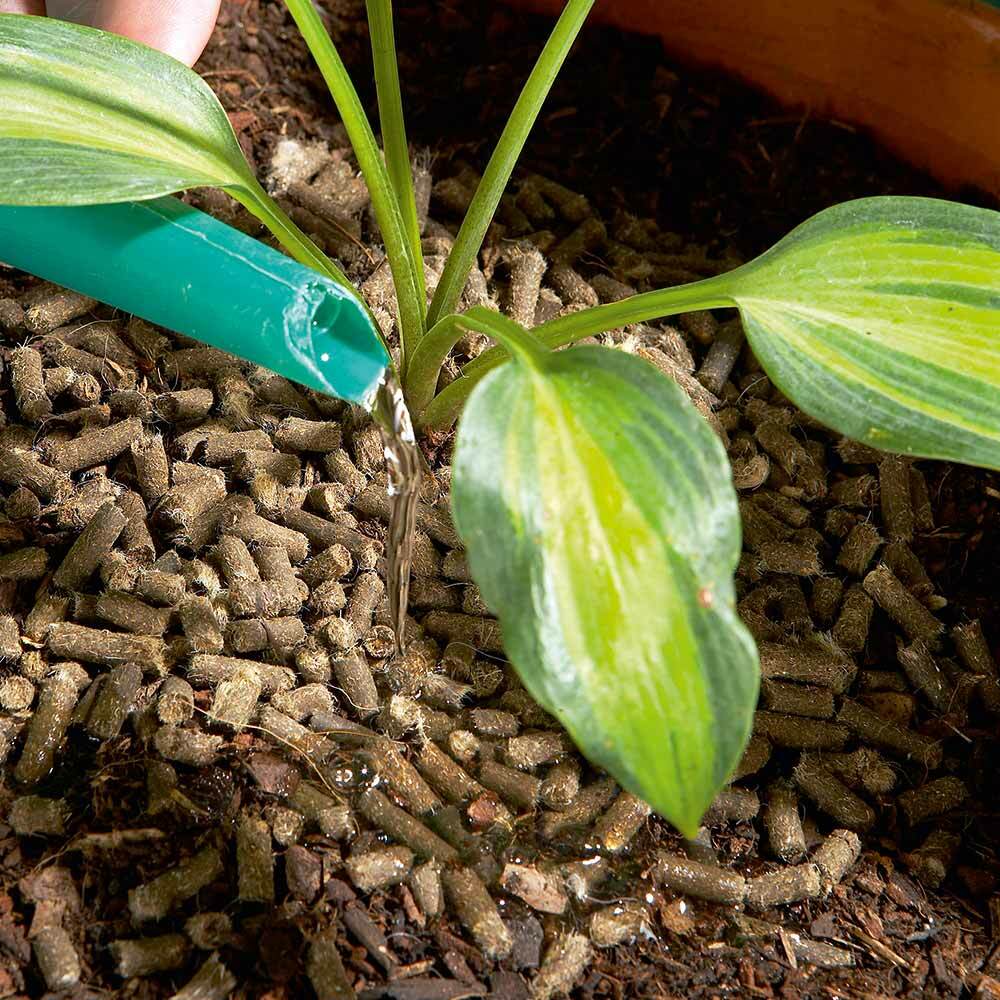



A wool layer applied to the soil surface, particularly in greenhouses or as a mulching material, minimizes temperature fluctuations in the topsoil. This creates a more stable thermal environment for plant roots.
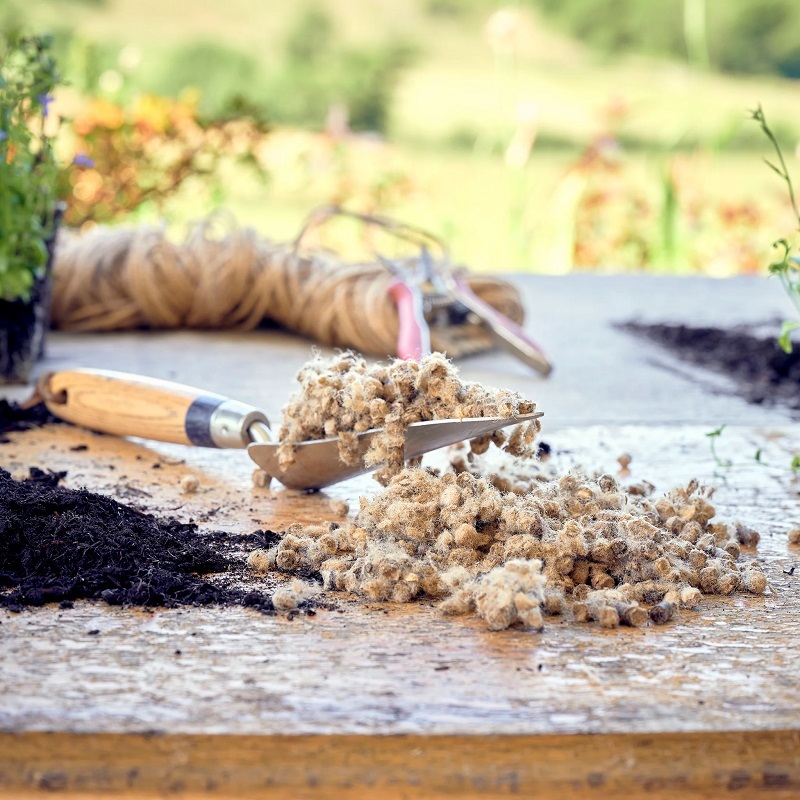
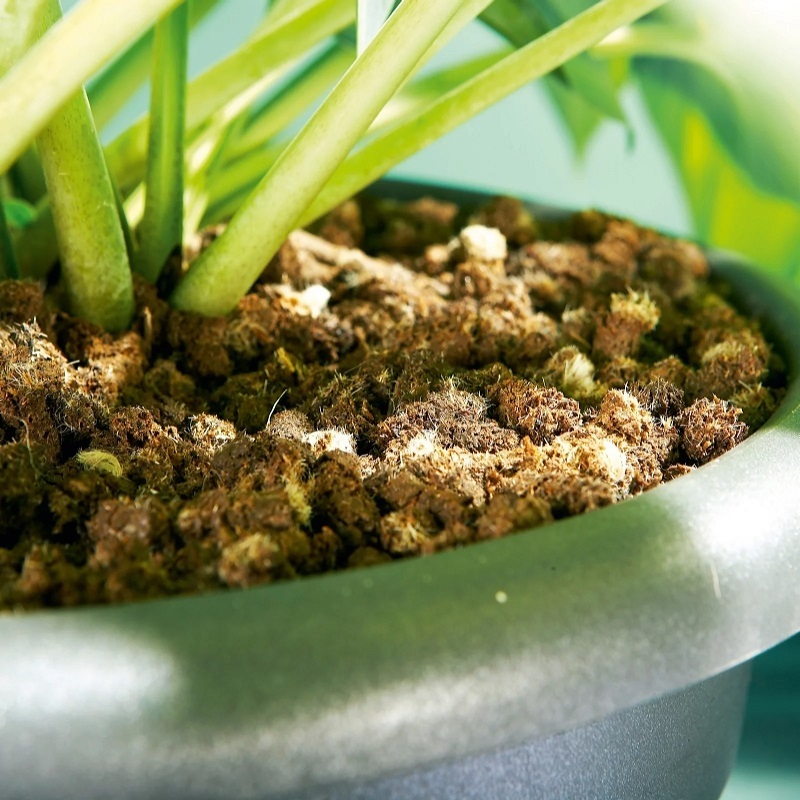


Wool can absorb up to 35% of its dry weight in moisture. When applied to the soil, this property helps regulate soil moisture levels
Slow Moisture Release:
Wool gradually releases the absorbed moisture back into the soil depending on environmental conditions. This ensures that the soil remains consistently moist, reducing evaporation, especially in dry periods, and making water use more efficient for plants.
Water Conservation:
By retaining soil moisture, wool applications reduce the frequency of irrigation, leading to significant water savings. This is particularly advantageous in regions experiencing water scarcity.
Protein-Based Structure:
Wool is primarily composed of keratin proteins. Due to its slow natural decomposition, it gradually releases organic matter and essential nutrients like nitrogen into the soil.
Long-Term Nutrient Source:
Since wool decomposes slowly, it does not provide an immediate nutrient boost but rather a long-term and sustained nutrient release, enhancing soil fertility over time.
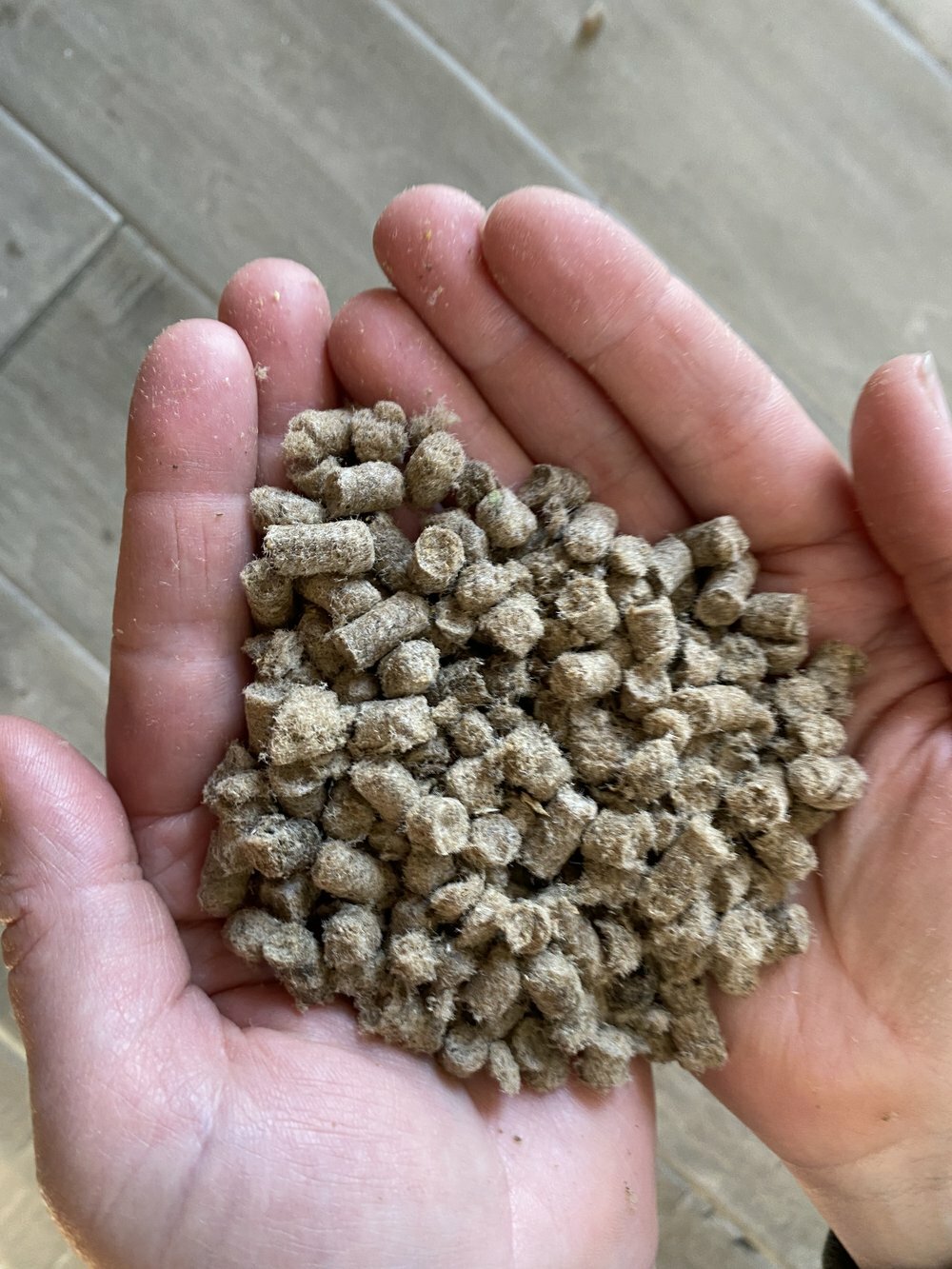
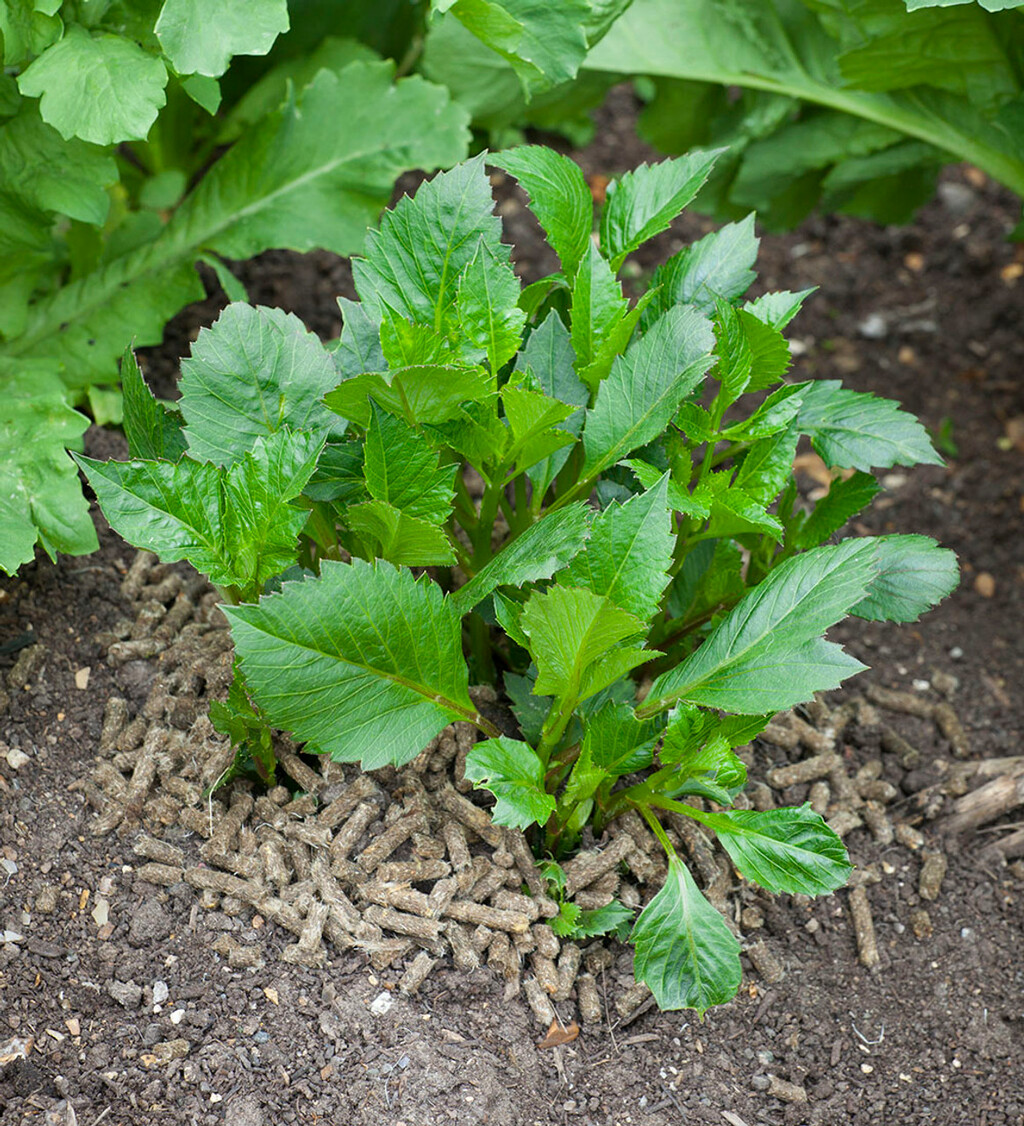


Organic Matter Contribution:
As wool fibers break down, they add organic matter to the soil. This strengthens the bonds between soil particles, increases water retention capacity, and improves soil aeration.
Increased Microbial Activity:
The added organic matter serves as a nutrient source for soil microorganisms. Enhanced microbial activity accelerates the breakdown of organic matter, improving soil health and plant nutrient availability.
Use in Greenhouses:
A wool layer applied to the greenhouse floor or plant beds helps maintain soil temperature and prevent moisture loss, creating optimal growing conditions for plants.
Mulching (Soil Covering Material):
When used as an organic mulching material, wool suppresses weed growth while regulating soil temperature and moisture levels.
As Organic Fertilizer:
Incorporating wool fibers into the soil provides a long-lasting organic fertilization effect, enhancing agricultural productivity and promoting healthier plant growth.
Water Management:
Wool applications help retain soil moisture, reducing irrigation needs and promoting more efficient use of water resources, especially in arid regions.


The addition of washed sheep wool to a peat-based growing medium provides significant benefits for vegetables such as tomatoes and sweet peppers. Research findings indicate that wool application increases tomato yield by 30%, while also enhancing yield and fruit count in sweet peppers. The slow-release nutrients from the wool, improved water retention, and stimulation of root development support plant growth, leading to healthier and greener leaves. These results highlight the potential of waste sheep wool as an organic fertilizer and soil conditioner, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices.
Reference: https://www.pjoes.com/pdf-88486-22345?filename=22345.pdf
Research and Developments in Sheep Wool Fertilizer:
Innovations and Applications for Sustainable Agriculture